This system enables real-time monitoring and automatic speed control of the conveyor, as well as product sorting using sensors. IoT plays a crucial role in providing real-time monitoring and remote control.
1. Planning & System Concept
Objective:
- Develop a smart conveyor system that can automatically control speed and sort products.
- Monitor the status and performance of the conveyor in real-time using the FAVORIOT IoT Platform.
Main Components:
- Microcontroller: Arduino / Raspberry Pi
- Sensor: IR (Infrared) sensor for object detection
- Servo Motor: To control product sorting
- FAVORIOT IoT: For remote monitoring and data analytics
- IoT Dashboard: Displays system status and controls
2. System Design
This system consists of two main parts:
- Physical System (Hardware)Conveyor with a servo motor for speed control
- IR sensor placed at the conveyor’s end to detect products
- Arduino/Raspberry Pi acts as the main controller
- IoT System (Software)Sensor data is sent to FAVORIOT via WiFi
- IoT Dashboard for data visualization and speed control
3. Hardware Development
(i) Electronic Connections
- IR Sensor → Detects products on the conveyor
- Servo Motor → Controls conveyor speed
- WiFi Module (ESP8266/ESP32) → Sends data to FAVORIOT
(ii) Connection Network
- IR Sensor ➝ Arduino ➝ WiFi Module ➝ FAVORIOT Cloud
- Arduino receives commands from the FAVORIOT Dashboard for speed control
4. IoT Integration with FAVORIOT
(i) Registering on the Favoriot IoT Platform
- Sign Up: Log in to the Favoriot IoT Platform
- Create a New Device:Device Name:
Smart_Conveyor_001An API Key will be provided for data transmission
(ii) Sending Data to Favoriot
Data format sent to Favoriot:
{
"device_developer_id": "Smart_Conveyor_001",
"data": {
"speed": 100,
"status": "Running",
"product_detected": 1
}
}
Use Arduino with ESP8266 or Raspberry Pi (Python MQTT/HTTP) to send data.
Example Code (Arduino + ESP8266)
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <ESP8266HTTPClient.h>
const char* ssid = "Your_WiFi_Name";
const char* password = "Your_WiFi_Password";
const char* server = "http://apiv2.favoriot.com/v2/streams";
const char* api_key = "YOUR_FAVORIOT_API_KEY";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000);
Serial.println("Connecting to WiFi...");
}
}
void loop() {
if (WiFi.status() == WL_CONNECTED) {
HTTPClient http;
http.begin(server);
http.addHeader("Content-Type", "application/json");
http.addHeader("Apikey", api_key);
String jsonData = "{\"device_developer_id\":\"Smart_Conveyor_001\",\"data\":{\"speed\":100,\"status\":\"Running\",\"product_detected\":1}}";
int httpResponseCode = http.POST(jsonData);
Serial.println(httpResponseCode);
http.end();
}
delay(5000); // Send data every 5 seconds
}
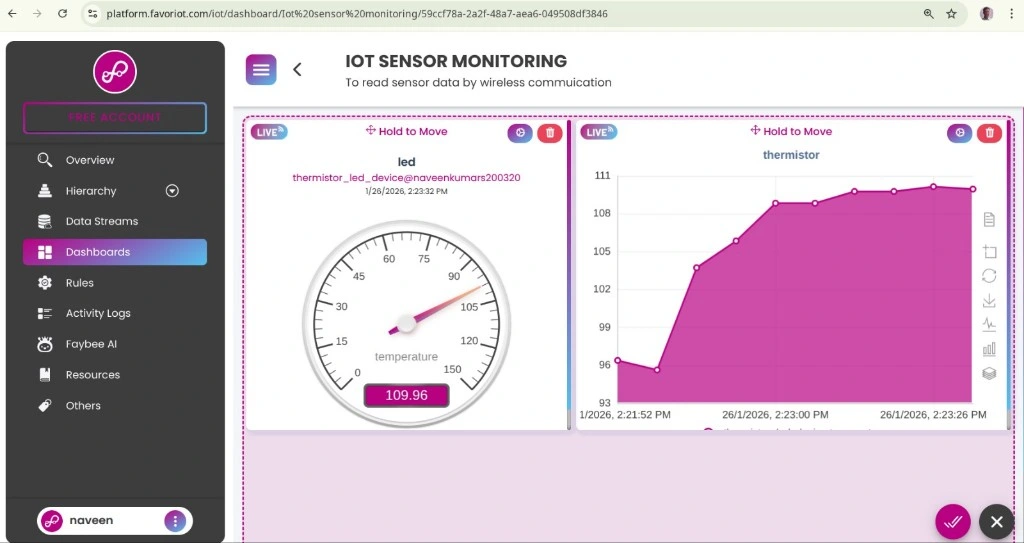
5. IoT Dashboard Development
Using the FAVORIOT Dashboard to:
- Monitor Conveyor Speed (Real-time speed monitoring)
- Machine Status (
Running/Stopped) - Product Count
The dashboard can be built using the FAVORIOT IoT Dashboard or integrated with Node-RED for a more customizable interface.
6. Remote Control via IoT
- Sending Speed Control Commands via FavoriotUse the Favoriot API to adjust conveyor speed remotely.
- Example: To change speed to 50%, send a POST request:
-
{ -
"device_developer_id": "Smart_Conveyor_001", -
"data": { -
"speed": 50 -
} -
} -
- Code to Receive Commands on Arduino
String speed_value = received_data["data"]["speed"]; -
int motorSpeed = speed_value.toInt(); -
analogWrite(motorPin, motorSpeed); -
7. Testing & Adjustments
After developing the system, conduct tests:
- IR Sensor Test – Ensure it accurately detects objects.
- Speed Control Test – Verify that the servo motor responds correctly to speed changes from the Favoriot Dashboard.
- IoT Data Transmission Test – Confirm that speed and status data are sent to Favoriot and displayed on the dashboard.
- Automation Simulation – Test the system with actual products to ensure correct sorting.
8. Conclusion & Future Enhancements
Project Benefits
✅ Real-Time Monitoring – Conveyor status can be monitored via the Favoriot Dashboard.
✅ Automated Production – Speed adjusts automatically based on sensor data.
✅ Remote Control – The system can be controlled from anywhere.
Future Improvements
📌 Integrate AI (Machine Learning) to optimize speed based on product volume.
📌 Use AI Camera for product recognition.
📌 Implement MQTT Technology for faster and more stable communication.
This project leverages FAVORIOT IoT as the main platform for monitoring and control. Proper integration can significantly improve automation and efficiency in the manufacturing industry!
[Disclaimer: This article provides a step-by-step guide. The source code may need adjustments to fit the final project design.]
![[Tutorial] : Smart Conveyor System with IoT Monitoring](https://iotworld.co/wp-content/uploads/2025/03/DALL·E-2025-03-16-07.10.26-A-professional-high-tech-image-of-a-Smart-Conveyor-System-with-IoT-Monitoring-using-the-Favoriot-dashboard.-The-conveyor-belt-is-equipped-with-infrar.webp)




Leave a Reply to DurgaCancel reply